ENT in NIRUJAA CLINIC
What do ENT surgeons do?
Our ENT (Otolaryngologist) clinic deals with the diagnosis, evaluation and management of diseases of head and neck and principally the ears, nose and throat.
One of the key areas of concern for ENT surgeons are helping patients cope with or recover from diseases that impair the senses of hearing and balance. They will also be concerned with the functional aspects of breathing, eating and speech. ENT surgeons also deal with cancers in this region of the body. Many will undertake plastic and reconstructive work on the face.
There are ten surgical specialties and this briefing covers otolaryngology, or ears, nose and throat (ENT) surgery.
ENT problems occur in all age groups but infective problems are particularly frequent in young people. Consequently, ENT surgeons see a much higher proportion of paediatric patients than any other branch of surgery, other than specialist paediatric surgeons.
Common Diseases in ENT
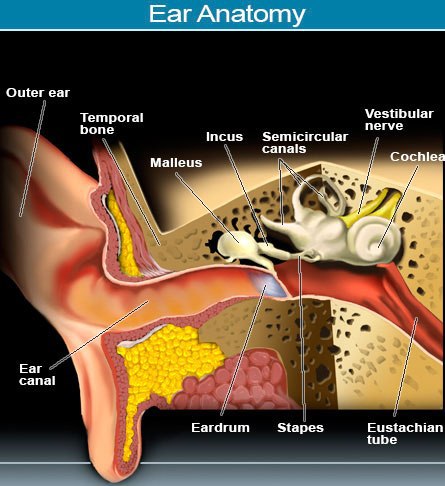

Disease of External Ear
The External Ear consists of the pinna and the External Auditory canal. Inflammatory disorder of the External Ear Canal is one of the common Ear problem affecting approximately 4 of every 1000 children and adults per year. 80% of the cases occur in in summer particularly in warm and humid environment other predisposing factors include obstruction of ear canal by impacted cerumen or wax, hearing aid or ear plug use, self-induced trauma and swimming, pathogenesis of inflammatory disorder include bacterial, fungi and other chronic causes which include allergic dermatitis, contact dermatitis(with shampoo and hair dye), psoriasis and granular dermatitis.
Pain is a common symptom, itching, decreased hearing or ear fullness and ear discharge are other symptom. Other common disorder of external ear includes Herpes Zoster infection, bullous myringitis, perichondritis,furunculosis, cellulitis of external ear, Erysipelas, Keratosis obturans and EAC Cholesteatoma

Disease of Middle Ear - (nakong leikhun)
It include disease involving the middle ear space. Otitis media(nakong leikhun) is the general term used for non-specific inflammation within the middle ear space. It include a broad range of pathological condition including Acute otitis media (AOM; suppurative and non suppurative) eosinophilic otitis media and chronic suppurative otitis media with or without cholesteatoma.
Otitis media is one of the most common infectious disease in young children. It can associated with speech, language and balance difficulties which can further contribute to learning problem. Sequele of otitis media not only result from auditory deprivation early childhood it can also cause serious complications like labyrinthitis, facial paralysis, erosion or fixation of ossicles, mastoid and cholesteatomas.
Earache, fever and ear discharge are common symptoms. Sometime present with hearing loss and dizziness.

Otosclerosis
An inherited disorder that causes hearing loss due to the ear's inability sound.
There are three small bones that connect to the ear drum to help amplify sound waves. Ossicular fixation occurs due to hormonal influence being common in females between 18 and 30 years. There appears to be a close relationship between the onset of deafness and the onset of puberty or occurrence of pregnancy.
Symptoms may include hearing loss or ringing in the ear. In other cases vertigo or dizziness may occur.

Disease of Inner Ear
The Inner Ear is in the petrous area of the temporal bone. Within the bone is the osseous labyrinth which in cases the membrane labyrinth. The osseous labyrinth include the vestibular system and the cochlea. The vestibular system is responsible for balance and positive and cochlea is responsible for hearing.
Inner Ear disorder can present as Dizziness or spinning sensation, nausea or vomiting, tinnitus and hearing loss.
Disorder of Nose and Paranasal Sinus
Common disorder of the Nose and Sinuses include Sinusitis, nasal polyposis, smell and taste disorder Epistaxis or bleeding from Nose and deviated nasal septum.
Sinusitis is often a chronic disease and may present as nasal obstruction, nasal discharge, and decreased sense of smell, facial pressure and fever. Sinusitis may be associated with allergic causes and also may be associated with anatomical cause's symptoms and sign for each condition differ and each diagnosis requires a unique treatment regimen.
After getting the correct diagnosis a number of medical treatments can be started which are often required on a long term basis. In some cases surgery is required the type of surgery which is minimally invasive and does not require external incision.
Nasal polyposis occur when the lining of the sinuses swell. Polyp may block the nasal airway, creating difficulty in breathing, polyps may also block the natural drainage of the sinus cavities leading to infection. Polyps are generally thought to occur as a result of an ongoing inflammatory process within the nose and sinus medication are tried as fine line therapy followed by surgery.
Smell and task disorder can have a large limp act on quality of life. It is estimated that upto 80% of task is a result of olfactory(smell) input. As a result loss of smell is frequently interpret as a loss of taste. Problem with smell and taste can be due to obstructive causes usually nasal in origin or functional which is neurological in origin.
Bleeding from Nose or Epistaxis is one of the common problem of nose. 70% of adult males over 60 years have had an epistaxis. The commonest cause is either external trauma or from picking the nose. Most epistaxis arise from little area not only because of highly vascular nature of the region but also inspired air tends to be directed onto it causing under drying and crusting. When this is removed some of the mucosa is after also removed to produce bleeding. The etiological factor for epistaxis include trauma, URTI, foreign bodies, post-operative nose or sinus infection, tumour, elevated blood pressure and disorder of blood vessels and clotting mechanism.
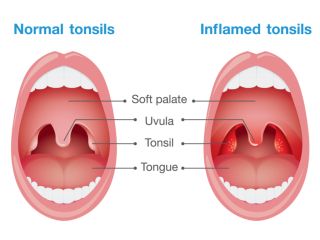
Tonsil and Adenoid related
Tonsil and adenoids are collection of lymphoid tissue that may have a role in helping the body fight infection. They trap bacteria and viruses entering through the throat and produce antibodies. Adenoids are a patch of tissue that is located just behind the nose and the tonsils are pair of lymphoid tissue located in the soft palate.
Chronic adenotonsillar hypertrophy in children is the most common indication for adenotonsillectomy. Typically the tonsil and adenoids are very small at birth and progressively enlarge over the first to fourth years of life as a result of immunologic activity. In addition to chronic infection, smoke exposure also has been impacted as a cause of adenotonsillar hypertrophy in children. The obstructive apnea is almost associated with the hypertrophy of tonsil and adenoids. The obstruction in sleep can result in a mildly comprised airway which is result in snoring as well as apnoea or oxygen desaturation.
Children sometime present with pulmonary hypertension, cor pulmonale, failure to thrive and developmental delay. Daytime sleepiness and behavioural difficulties are the most common sequence of obstructive sleep apnoea caused by tonsil and adenoid enlargement.
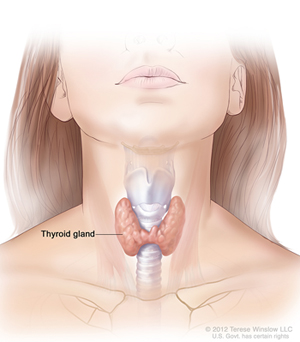
Thyroid Disorder
The thyroid gland which is located in the lower anterior neck in close relationship to the larynx, the trachea and oesophagus has a profound effect on all bodily functions. Thyroid disease are relatively common. They occur in the form of neck swelling and of abnormalities of the thyroid secretion i.e., either excessive thyroid secretion(hyperthyroidism) or reduced thyroid secretion (hypothyroidism)
Generalised symptoms relating to hypothyroidism, include weakness and fatigue with cold intolerance, weight gain, hair loss, edema of the face and hands, thick, dry skin, hair and decreased sweating. ENT symptoms may include hearing loss, tinnitus, voice aberrations, slurred speech and enlarged tongue. The GI symptoms include constipation, anorexia. Genitourinary symptoms include menstrual disorders and a tendency toward polyuria, CVS symptoms include bradycardia. High BP CNS sympyoms include daytime somnolence but insomnia at night. Last but not the least it may present with musculoskeletal symptom include arthritis and stiffness of the joints.
The general symptoms of hyperthyroidism commonly include a rapid heartbeat palpitation, irritability, anxiety, easy fatigue, weight loss and heat intolerance. Patient may present with lid lag, eyelid retraction and exophthalmos.